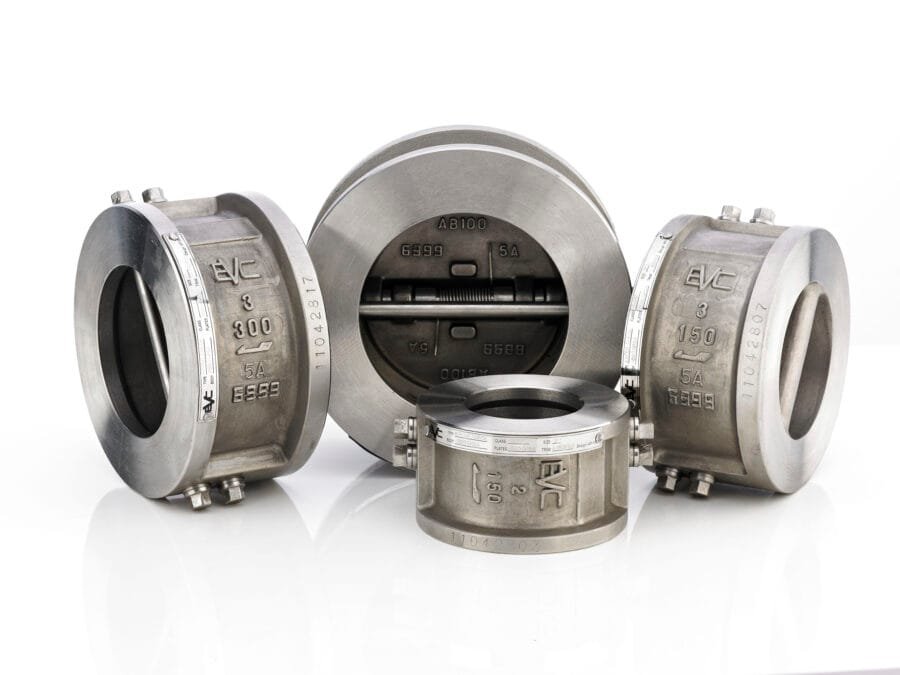
Wafer Check Valve – Edmund Valve Company Ltd
The wafer check valve is a compact unidirectional valve designed to effectively prevent fluid backflow, making it widely used in space-constrained piping systems. Named “wafer” due to its thin, disc-like design, it is installed directly between two flanges, ensuring a space saving solution for modern piping layouts. With its lightweight construction and efficient functionality, this valve holds a significant position in both industrial and commercial applications.
Table of Contents
Working Principle of Wafer Check Valves
The core components of a wafer check valve include the disc, spring, and seat. Its working mechanism operates as follows:
- Forward Flow: When fluid flows in the designated direction, the fluid pressure pushes the disc open, allowing the fluid to pass through.
- Reverse Flow: When fluid flows in the reverse direction or pressure drops, the spring in the reliable check valve quickly pushes the disc back onto the seat, forming a seal to prevent backflow.
This simple mechanical structure ensures stability and reliability while minimizing maintenance requirements.
Advantages of Wafer Check Valves
Compared to other types of check valves, wafer check valves offer several notable advantages:
- Compact Design: The ultra-thin profile saves installation space.
- Lightweight: Facilitates transportation and installation while reducing the overall load on the piping system.
- Low Pressure Loss: Optimized flow path design minimizes system pressure drop.
- Wide Applicability: Suitable for handling various media, including water, oil, and gas.
- Cost-Effective: Lower material and maintenance costs compared to more complex valves.
Applications of Wafer Check Valves
Dawal wafer check valves are suitable for a variety of fields. Here are some typical applications:
- Industrial Water Treatment: Preventing backflow in pumping systems to protect equipment.
- HVAC Systems: Ensuring unidirectional flow of cooling or heating media.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Preventing fluid backflow in transportation pipelines.
- Chemical Industry: Protecting sensitive equipment from the effects of reverse flow.
- Marine Engineering: Used in ballast and bilge water treatment systems on ships.
Common Types of Wafer Check Valves
Based on differences in structure and functionality, wafer check valves can be categorized into the following types:
- Single Disc Check Valve: Features a single disc design, suitable for standard applications with a simple and reliable structure.
- Dual Plate Check Valve: Equipped with dual plates that fold inward during forward flow, effectively reducing water hammer effects.
- Spring-Loaded Check Valve: Incorporates a spring mechanism for rapid disc closure, ideal for applications requiring frequent opening and closing.
Size and Pressure Range of Wafer Check Valves
Size Range: 1/2″ – 48″ (DN15 – DN1200)
Pressure Range: Class 150 – Class 2500 (PN20 – PN420)
Connection Type of Wafer Check Valves
Wafer Type Check Valve
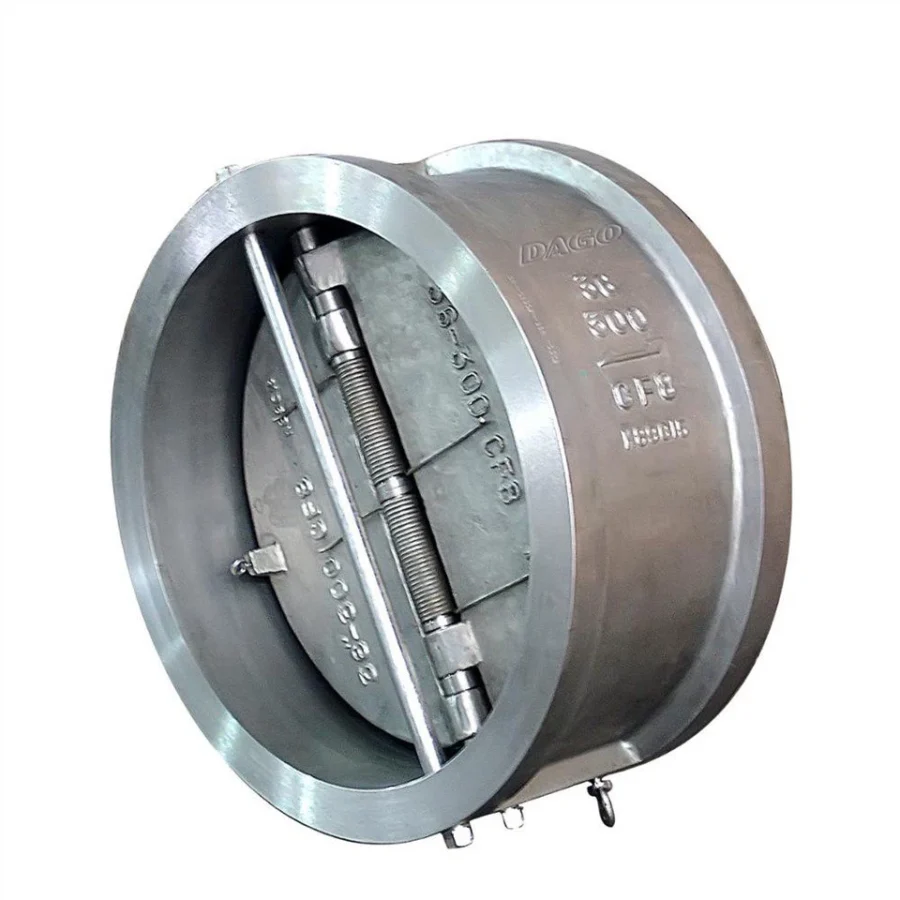

This is the most common connection method, as wafer check valves are renowned for their compact design:
- Slim and Lightweight Body: The valve is sandwiched between two flanges.
- Secured with Flange Bolts: Fixed in place without requiring additional support structures.
Applicable Scenarios: Pipeline systems with space or weight constraints, such as industrial production lines and building water supply systems.
Advantages: Simple structure, easy installation, and cost-effective space-saving design.
Lug Type Wafer Check Valve

The raised-face connection features bolt holes around the wafer lug check valve body for direct connection to pipeline flanges:
- Threaded Holes on the Body: Allow for one-sided disassembly, offering greater flexibility for maintenance.
- Slightly Heavier than Wafer Type: Provides enhanced stability.
Applicable Scenarios: Systems requiring frequent disassembly and maintenance or pipelines demanding higher support strength.
Advantages: Supports blind-end use, maintaining a seal even when connected to a flange on only one side.
Welded Check Valve Wafer Type

Welded connection is a permanent joining method:
- Welded to the Pipeline: The valve body is secured to the pipeline through welding, eliminating the need for flanges or bolts.
- Ideal for High-Pressure, High-Temperature Applications: Ensures durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
Applicable Scenarios: Nuclear power plants, natural gas transmission, and other environments with stringent sealing requirements.
Advantages: Completely eliminates leakage, resulting in a more compact structure.
Disadvantages: Difficult to disassemble and maintain, requiring a high level of technical expertise for installation.
Threaded Type Wafer Check Valve

Threaded check valve | Fitting Service
Check valves threaded are designed with threads on both ends of the valve body.
- Direct Connection: Designed to connect directly to threaded pipelines without requiring flange fittings.
- Suitable for Small-Diameter Pipelines: Commonly used in compact piping systems.
Applications: Household water supply, laboratory gas transmission, and other small-scale systems.
Advantages: Quick to install and ideal for low-cost applications.
Material Selection for Wafer Check Valves
Wafer check valves are available in a variety of materials to suit different operating conditions:
- Body Materials: Stainless steel, carbon steel, PVC, ductile iron, etc.
- Disc Materials: Stainless steel, bronze, or composite materials for enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Seal Materials: Commonly EPDM, Viton, or PTFE, ensuring excellent sealing performance.
Material selection should be optimized based on the chemical properties of the medium, as well as the operating temperature and pressure.
Installation Considerations for Wafer Check Valves
Proper installation of a wafer check valve is critical to its performance:
- Confirm Flow Direction: Install the valve according to the flow direction indicated on the valve body to ensure one-way flow.
- Pipe Alignment: Ensure the pipe flanges are properly aligned to prevent stress concentration that could damage the valve body.
- Bolt Tightening: Evenly tighten the flange bolts to maximize sealing performance.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly check the condition of the disc and spring, especially in systems with frequent opening and closing cycles.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Wafer Check Valves
Although wafer check valves require minimal maintenance, regular upkeep can extend their service life:
- Regular Cleaning: Remove debris inside the valve to prevent blockages.
- Seal Inspection: Check the condition of the sealing elements and replace worn components promptly.
- Spring Check: Ensure the spring in a spring wafer check valve maintains its elasticity to prevent sealing failure caused by fatigue.